Researchers from Yale School of Forestry and Environmental Studies dig deeper into homosexual tendencies in animals.
Homosexuality in animals, why not?
Homosexuality. A romantic or sexual attraction towards the same sex.
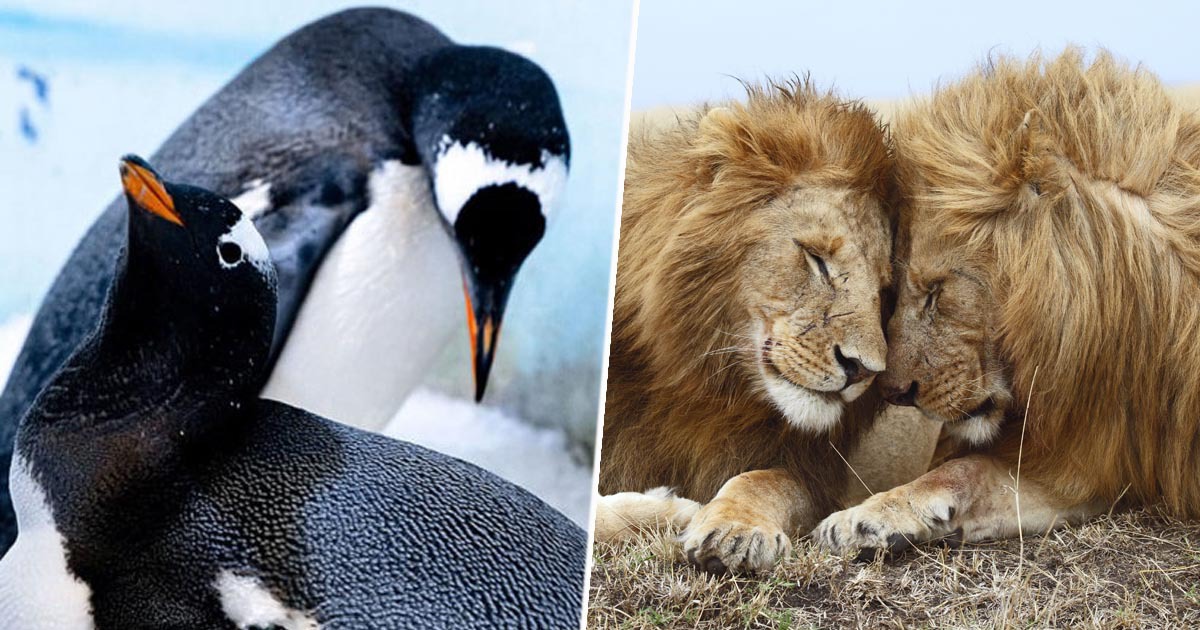
Homosexual behavior in animals. According to research, around 1,500 species of animals have a homosexual orientation. This is a puzzling event for scientists trying to analyze why so many species opt to develop a behavior that results in no offsprings. Is this what the Darwinian Paradox of Homosexuality has projected to be?
The Darwinian Paradox of Homosexuality
The explanation for homosexuality is still elusive, but there is an interesting study of its biological basis. Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), researchers identified brain structures of heterosexuals and homosexuals. According to the images, the brain structure of heterosexual men and homosexual women have a slightly larger right hemisphere compared to homosexual men and straight women.
Brain structure is just one of the few supporting data that sexual orientation can be biological in nature. Though the idea of environmental influence is also considered, the case of “choice” has gradually decreased in merit.

Nature Ecology and Evolution
Researchers from Yale came out with an article titled Nature Ecology and Evolution. In this paper, they suggested that the earliest ancestral sexual behavior was directed towards all sexes. It was not purely heterosexual or even homosexual.
As part of evolution, several species found out that homosexual behavior is less beneficial and does not result in offspring, these species then prioritize a heterosexual behavior in their system.
Researchers claim that even though some species of animals are heterosexual, their homosexual nature is still innate in them. They just favor the former behavior to generate offsprings.
In groups of animals, there are always those that possess homosexual behavior. They also play a big part in the continuation of their species, it might not be reproductivity but in some other way.
A pack of wolves only have the alpha and the beta responsible for reproduction in the pack, while the rest provides food and protection for the young ones. Same goes with elephants, female elephants that are too old to give offsprings acts as matriarch to young calves. The inability to provide offspring gives them more energy to serve and provide the needs of the family.
Researchers believe that both heterosexual and homosexual behavior in animals plays a vital role in the continuation of their species. Sexual behavior not related to reproduction will not be eliminated by natural selection because every orientation serves a purpose in a species continuity, directly or indirectly.